23 Essential Terminologies of Cloud computing
Introduction
In this article,
you will be able to know and learn about some essential terminologies related
to cloud computing and AWS (Amazon Web Services).
Datacenter
·
Data center refers to a large group of
networked computer servers typically used by organizations for the remote
storage, processing, or distribution of large amounts of data.
·
Data center is a facility that provides
shared access to applications and data using a complex network, computing, and
storage infrastructure.
·
A modern data center houses an
organization’s data systems in a well-protected physical and storage
infrastructure along with servers, storage systems, networking switches,
routers, firewalls, cabling, and physical racks.
Cloud
· A cloud is a type of server, which is remote (usually in data centers) meaning you access it via the internet.
·
You are renting the cloud server space,
rather than owning the server.
·
Large clouds often have functions
distributed over multiple locations, each of which is a data center.
·
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the world’s
most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform.
Cloud server
·
A cloud server is a pooled, centralized
server resource that is hosted and delivered over a network-typically the
internet and accessed on demand by multiple users.
·
Cloud servers can deliver processing
power, storage, and applications.
·
The primary function of a cloud server is
storage.
·
Cloud servers avoid the hardware issues
seen with physical servers.
·
Cloud servers provide more resources and faster service.
·
Cloud servers are very easy and quick to
upgrade by adding memory and disk space.
·
Cloud servers are stable, fast, and
secure.
·
A cloud-hosted website runs fast.
·
Cloud servers are more affordable.
·
Cloud server is most often a mighty virtual IT infrastructure that can host data, applications,
information, and other components.
·
Some common examples of Cloud servers are
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances, Microsoft Azure instances, and
Google computes engine instances.
Cloud region
Cloud region
refers to the actual, real-life geographic location of your public cloud resources.
Cloud zones
·
Cloud regions are collections of zones.
·
Cloud zones have high bandwidth and low-latency network connections to other zones in the same region.
Cloud computing
·
Cloud computing is the on-demand
availability of computer system resources especially data storage and computing
power, without direct active management by the user.
·
Cloud computing is the delivery of
computing services – including servers, storage, databases, networking,
software, analytics, and intelligence- over the internet (“the cloud”) to offer
faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
·
Cloud computing makes data backup,
disaster recovery, and business continuity easier and less expensive.
·
Companies involved in cloud computing are
Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM.
A brief history of cloud computing
Cloud computing
was invented by JCR Licklider (Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider) in the early
1960s.
Different types of Cloud computing are:
Private cloud
· Private cloud refers to a cloud computing model where the infrastructure is dedicated to a single-user organization.
·
A private cloud serves a single client
organization (tenant), and is managed by a third party.
·
A private cloud is a service that is
completely controlled by a single organization and not shared with others.
·
Some common examples of private cloud are
HPE GreenLake and Azure stack.
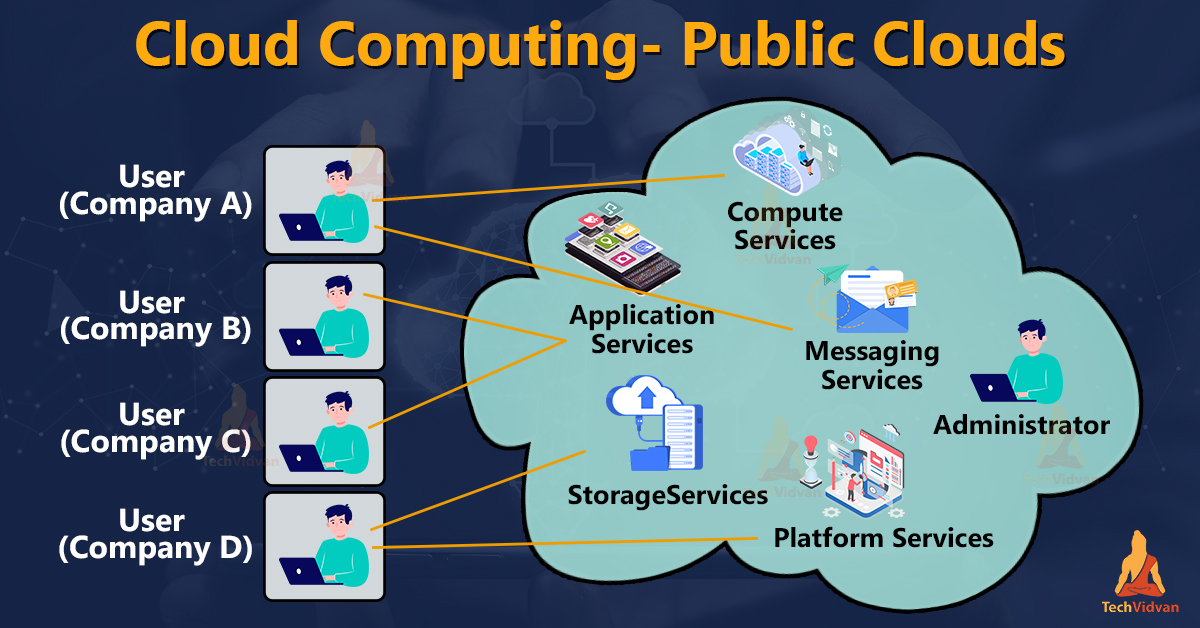
Public clouds
·
A public cloud refers to an IT model
where on-demand computing services and infrastructure are managed by a
third-party provider and shared with multiple organizations using the public
internet.
·
A public cloud shares the same hardware,
storage, and network devices with other organizations or cloud “tenants” and
manages accounts using a web browser.
·
Public cloud service providers use groups
of data centers that are partitioned into virtual machines and shared by
tenants.
·
Public cloud service providers offer
cloud-based services like infrastructure as a service (IaaS), Platform as a
service (PaaS), or software as a service (SaaS) to users for either a monthly
or pay-per-use fee.
·
A public cloud is a subscription service that is offered to anyone and all
customers who want similar services for purchase.
·
A public cloud eliminates the need for
users to host the cloud-based services on-site in their own data center.
·
Microsoft Azure is an example of a public
cloud.
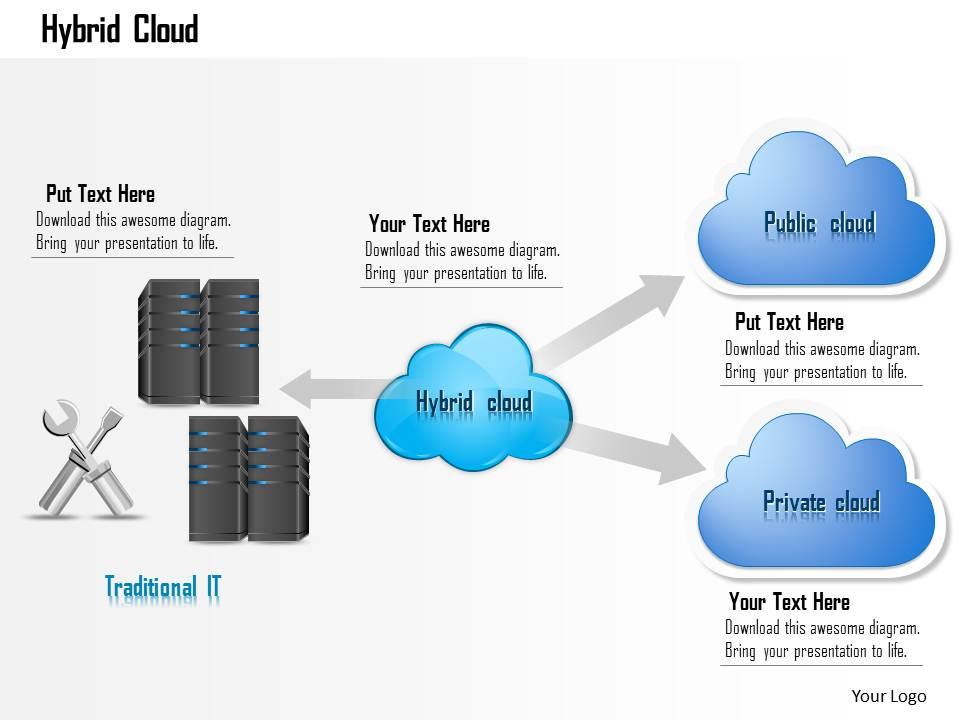
Hybrid clouds
·
Hybrid cloud is an IT infrastructure that
connects at least one public cloud and at least one private cloud and provides
orchestration, management, and application portability between them to create a
single, flexible, optimal cloud environment for running a company’s computing
workloads.
·
AWS storage gateway is a hybrid storage
service that enables on-premises workloads to use AWS cloud storage. Capabilities
such as File Gateway, Tape Gateway, and volume Gateway help manage hybrid cloud
workloads, backup and restore, and disaster recovery use cases.
Multi-clouds
·
Multi-cloud refers to the presence of
more than one cloud deployment of the same type (public or private) sourced
from different vendors.
·
A multi-cloud strategy gives companies
the freedom to use the best possible cloud for each workload.
·
For example, a business might use AWS for
data storage, Google cloud platform for development and testing, and Microsoft Azure for disaster recovery.
Cloud migration
· Cloud migration refers to the process of moving a company’s digital assets, services, databases, IT resources, and applications either partially or wholly, into the cloud.
· Cloud migration is also about moving from one cloud to another.
AWS
·
AWS stands for Amazon Web Services.
·
AWS is a subsidiary of Amazon.
·
AWS provides on-demand cloud computing
platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered
pay-as-you-go basis.
·
AWS provides distributed computing processing
capacity and software tools via AWS server farms.
·
In 2006, AWS began offering IT
infrastructure services to businesses in the form of web services now commonly
known as cloud computing.
·
AWS is the world’s most comprehensive and
broadly adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from
data centers globally.
· AWS includes a mixture of infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and packaged software-as-a-service (SaaS) client-server technology- the relationship between a client (your laptop browser) and the server (the machine sitting on the back end and receiving your browser requests). These services are also referred to as cloud service models or cloud computing service models.
Different types of Cloud computing services are:
IaaS
·
IaaS is a cloud computing service model
by means of which computing resources are supplied by a cloud service provider.
·
The IaaS vendor provides storage,
network, servers, and virtualization.
·
Some popular examples of IaaS include
AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Digital Ocean, and Linode.
·
The first major provider of IaaS was
Amazon in 2008.
PaaS
PaaS is a
category of cloud computing services that allows customers to provision,
instantiate, run, and manage a modular bundle comprising a computing platform
and one or more applications.
SaaS
·
SaaS is also known as “on-demand software”
and web-based/web-hosted software.
·
SaaS is a software licensing and delivery
model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally
hosted.
·
SaaS is a way of delivering applications
over the internet as a service.
·
SaaS is a form of cloud computing that
delivers an application and all its underlying IT infrastructure and platforms
to users.
·
SaaS allows users to connect to and use
cloud-based apps over the internet.
·
Some common examples of SaaS services are
office 365 and Google docs, customer relationship management software (salesforce), and event management software (planning pod).
·
Examples of popular SaaS providers
include Big Commerce, Google workspace, and salesforce.
Modern
threats with SaaS-delivered security
The top seven SaaS security risks are:
· Misconfigurations
· Access management
· Regulatory compliance
· Data storage
· Data retention
· Privacy and data
breaches
· Data Disaster
Different types of storage in AWS
Object storage
·
Object storage is also known as
object-based storage.
·
Object storage is a computer data storage
architecture designed to store and manage large amounts of unstructured data. Unstructured
data can be photos, videos, emails, web pages, sensor data, and audio files.
·
Cloud object storage systems distribute unstructured
data across multiple physical devices but allow users to access the content
efficiently from a single, virtual storage repository.
·
Object storage combines the pieces of
data that make up a file, adds all the user-created metadata to that file, and
attaches a custom identifier.
File storage
·
Cloud file storage is a method for
storing data in the cloud that provides servers and applications access to data
through shared file systems.
·
Cloud file storage is ideal for workloads
that rely on shared file systems and provides simple integration without code
changes.
·
Cloud file storage system stores data in
a specific environment.
·
In a Cloud file storage system, data is
stored as files in a single piece.
·
Cloud file storage only provides one
path.
Block storage
·
Block storage is a cloud storage form used to store data, often on storage area networks (SANs).
·
Block storage systems can be integrated
with different operating systems.
·
In block storage, data is stored in
blocks.
·
Block storage architecture provides
multiple paths to the data.
·
Block storage is preferred for high-performance applications.
AWS Cloud 9 Software
·
AWS Cloud 9 Software is a cloud-based
integrated development environment (IDE) that lets you write, run, and debug
your code with a browser.
·
AWS Cloud 9 Software combines the rich
code editing features of an IDE such as code completion, hinting, and
step-through debugging, with access to a full Linux server for running and storing
code.
Amazon EC2
·
Amazon EC2 stands for Amazon Elastic
Compute Cloud.
·
Amazon EC2 provides scalable computing
capacity in the AWS cloud.
· Amazon EC2 is a general-purpose compute-optimized, memory-optimized, storage-optimized, and accelerated computing.
·
Amazon EC2 can be used to launch as many
or as few virtual servers as you need, configure, secure, network, and
manage storage.
·
Amazon EC2 eliminates your need to invest
in hardware upfront, so you can deploy applications faster.
· Amazon EC2 is a web service that provides resizable computing capacity-literally servers in Amazon’s data centers.
·
Amazon EC2 provides the broadest and
deepest instance choice to match your workload’s needs.
Amazon EC2 instance
·
Amazon EC2 instance is a virtual machine
that represents a physical server for you to deploy your applications.
·
Amazon EC2 provides different instance
types to enable you to choose the CPU, memory storage, and networking capacity
that you need to run your applications.
·
Amazon EC2 supports on-demand instances (the
default), spot instances, and reserved instances.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
·
Amazon EBS provides block-level storage
volumes for use with EC2 instances.
·
Amazon EBS volumes behave like raw,
unformatted block devices.
AWS region
·
AWS region is a separate geographic area.
·
Each AWS region has multiple, isolated
locations known as availability zones.
EDR
· EDR stands for
Endpoint Detection and Response.
· EDR is used for
continuous monitoring of end-user devices (computers and servers) to detect and
respond to cyber threats.
· Endpoint logs and
EDR monitoring generate alerts but they often do not provide sufficient detail
to contextualize the alerts received.
MSS
· MSS stands for Managed
Security Services.
· MSS is used to
effectively respond to modern threats.
· MSS is evolved to
deliver a new breed of holistic solutions: MDR and XDR.
MDR
· MDR stands for
Managed Detection and Response.
· MDR is a complete
monitoring of a network and alert escalation to full remediation of security events
detected.
· An MDR solution
improves the signal-to-noise ratio of alerts, closing telemetry gaps, and
narrowing talent gaps.
XDR
· XDR stands for
Extended Detection and Response.
· XDR combines data
from multiple sources, almost always including EDR, but often including data
from other systems.
· XDR platforms
incorporate data from multiple sources, including cloud platforms, email,
network traffic capture, EDR, and endpoint logs, enabling MDR providers to
contextualize alerts the same way their customers do.
Endpoint
in AWS
· An endpoint in
AWS is the URL of the entry point for an AWS web service. The AWS SDKs and the
AWS command line interface (AWS CLI) automatically use the default endpoint for
each service in an AWS region.
· Endpoints in AWS
are physical devices that connect to and exchange information with a computer
network.
· Some examples of
endpoints in AWS are mobile devices, desktop computers, virtual machines,
embedded devices, and servers.
Weaponizer
in AWS
Weaponizer in AWS is an all-in-one
solution for weapon design, as a VST/AU/AAX.
CKC
· CKC stands for
Cyber Kill Chain
· CKC is developed
by Lockheed Martin (2011).
· The CKC outlines
the various stages of several common cyber-attacks and, by extension, the
points at which the information security team can prevent, detect or intercept
attackers.
To know more visit https://zueducator.blogspot.com








No comments:
Post a Comment